User registration
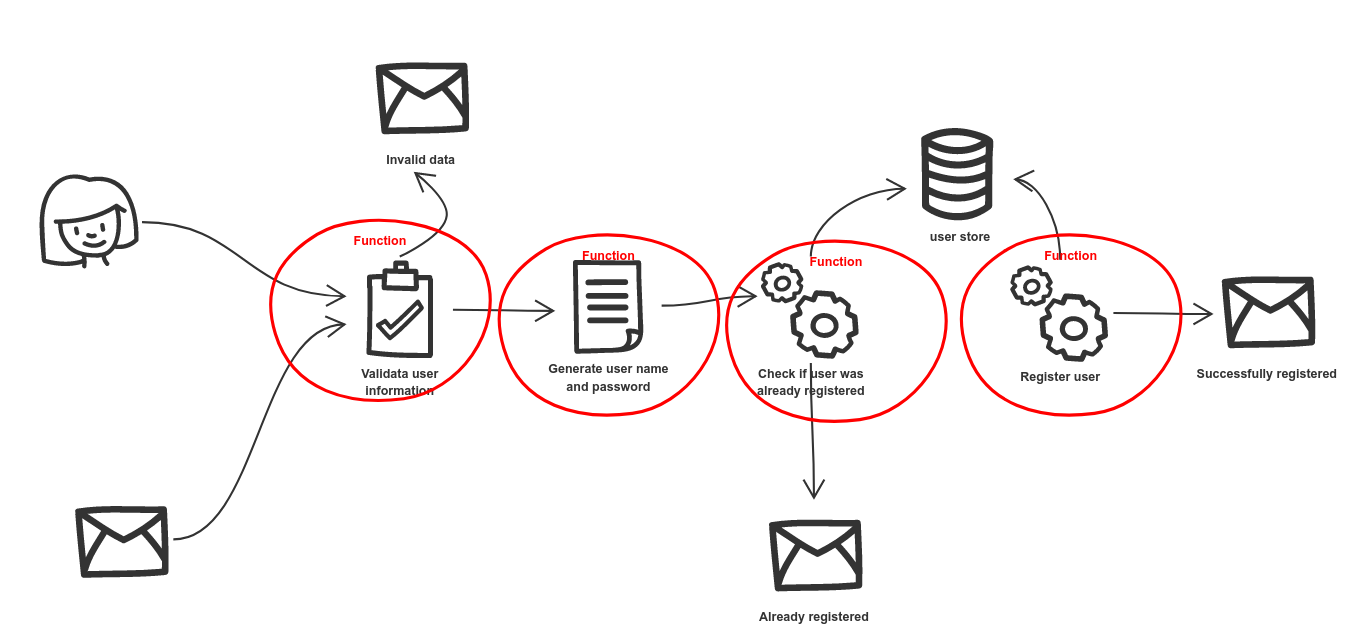
User registration example illustrates Workflow as a Function Flow concept that breaks down a workflow
definition into functions and automatically invokes them by emitting events (in cloud event format).
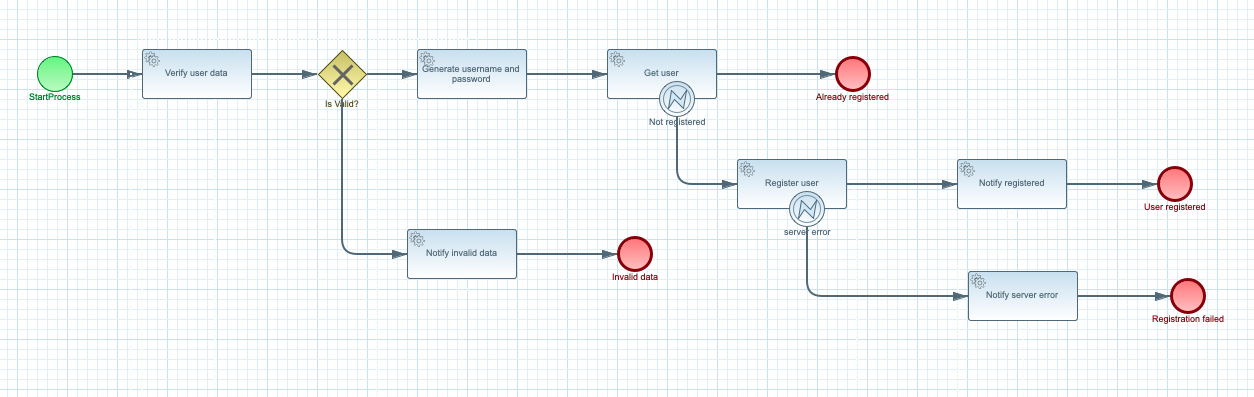
This example takes a simple user registration use case and implements it as workflow. The logic behind is composed of
-
validating provided user information
-
generating username and password
-
verifying that given user name is not yet registered in the Swagger PetStore service
-
creating user in the Swagger PetStore service
So the workflow defines multiple types of operations that are being invoked, starting from java services implemented within the service and finishing at REST invocation based on OpenAPI definitions.
In addition to that REST calls are equipped with error handling to tackle unexpected responses like server errors during creation of a user in Swagger PetStore service or expected situations like user not found in Swagger PetStore service.
Run it
There are multiple paths that can be taken during the user registration
Here is the functions that are broken out of the workflow
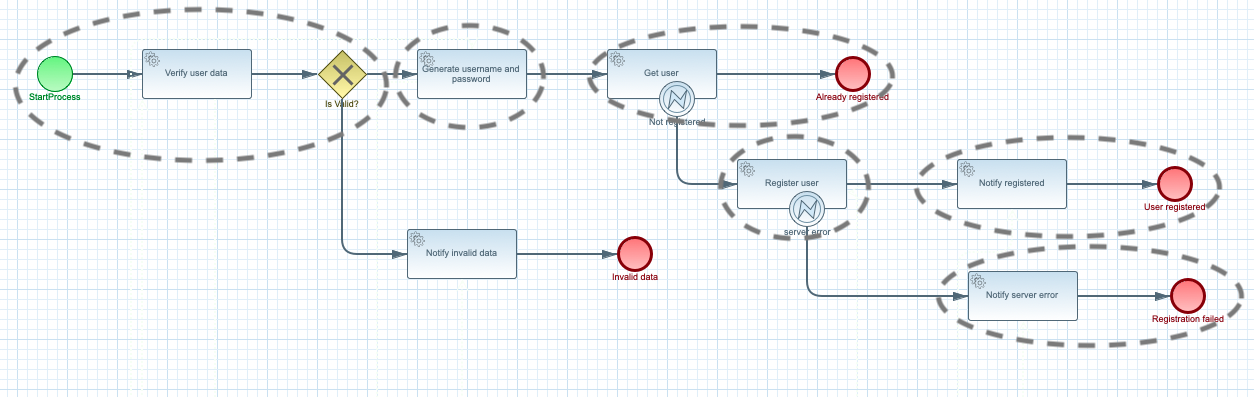
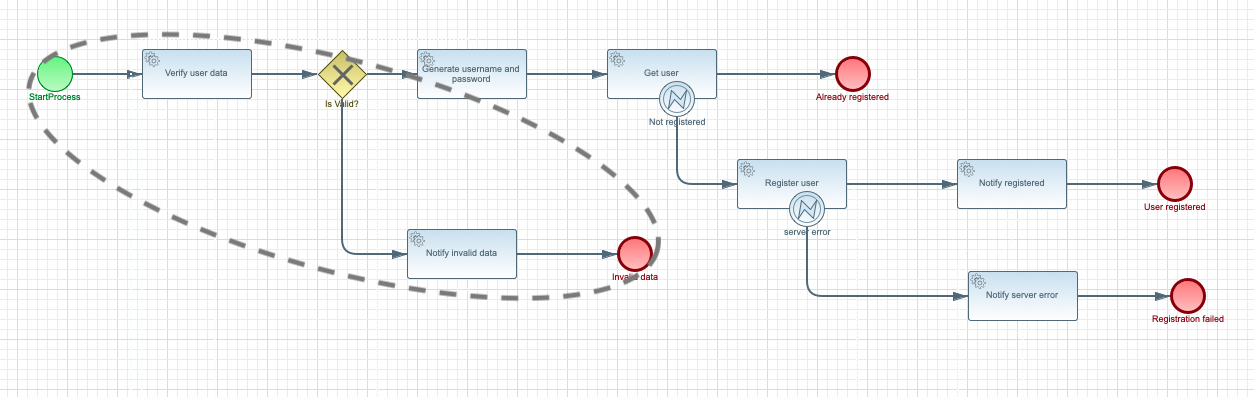
A surprising might be that the Notify invalid data is not selected as a function. The reason is that
the Notify invalid data is combined with Verify user data into single function to show case ability
of being able to control which activities are included in single function.
To be able to run it a Kubernetes cluster must be available with KNative Eventing installed. It could be local installation, such as
-
Minikube
-
Kind
or it can be cloud based Kubernetes cluster like
-
Google Kubernetes Engine
-
OpenShift
-
Azure kubernetes Engine
-
others
To install KNative, look at official documentation
Once the Knative and Kubernates cluster is available you can deploy the example by invoking following commands
kubectl apply -f k8s/user-registration.yamlHere is a content of the file for quick reference
apiVersion: sources.knative.dev/v1beta1
kind: SinkBinding
metadata:
name: bind-user-registration
spec:
subject:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: user-registration
sink:
ref:
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Broker
name: default
---
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: user-registration
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: user-registration-v1
annotations:
autoscaling.knative.dev/target: "1"
spec:
containers:
- image: automatiko/user-registration
---
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: userregistration
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: user-registration
---
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: getuser
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration.getuser
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: user-registration
---
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: notregistered
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration.notregistered
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: user-registration
---
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: generateusernameandpassword
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration.generateusernameandpassword
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: user-registration
---
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: registeruser
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration.registeruser
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: user-registration
---
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: notifyregistered
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration.notifyregistered
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: user-registration
---
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: notifyservererror
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration.notifyservererror
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: user-registration
---
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: servererror
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration.servererror
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: user-registrationOptionally you can also deploy event displayer to see all events flowing through the Knative broker
kubectl apply -f - << EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: event-display
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels: &labels
app: event-display
template:
metadata:
labels: *labels
spec:
containers:
- name: event-display
image: gcr.io/knative-releases/knative.dev/eventing/cmd/event_display
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: event-display
spec:
selector:
app: event-display
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
EOFDeploy the trigger for event displayer that will simply consume all events as there is no filter defined
kubectl apply -f - << EOF
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: event-display
spec:
broker: default
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: event-display
EOFGet the url of the default broker use following command
kubectl get broker defaultwhich should produce similar output
NAME URL AGE READY REASON
default http://broker-ingress.knative-eventing.svc.cluster.local/knativetutorial/default 140d TrueThe happy path
Happy path consists of steps that will lead to successful user registration.
Try it
Follow steps in the Details section to see the happy path in action.
| Login to a curler pod that enables an easy access to the broker to send requests as it might not be exposed to external traffic (e.g. ingress). If your Knative broker is exposed to external traffic you can skip the curler step. |
Issue following curl command from the pod running within cluster so the broker url will be properly resolved.
curl -v "http://broker-ingress.knative-eventing.svc.cluster.local/knativetutorial/default" \
-X POST \
-H "Ce-Id: 1234" \
-H "Ce-Specversion: 1.0" \
-H "Ce-Type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration" \
-H "Ce-Source: curl" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"user" : {"email" : "mike.strong@email.com", "firstName" : "mike", "lastName" : "strong"}}'This will send a request to the broker using HTTP binary binding for cloud events. The cloud events information
are given http headers prefixed with ce-.
Taking into consideration that this request was sent for the first time it should register user in Swagger PetStore.
| It might result in a already registered when the user was already registered so consider updating the first name and last name in the request payload with custom data that will ensure new user |
The invalid data path
Invalid data path consists of steps that will lead to fast finish without user registration.
Try it
Follow steps in the Details section to see the invalid data path in action.
| Login to a curler pod that enables an easy access to the broker to send requests as it might not be exposed to external traffic (e.g. ingress). If your Knative broker is exposed to external traffic you can skip the curler step. |
Issue following curl command from the pod running within cluster so the broker url will be properly resolved.
curl -v "http://broker-ingress.knative-eventing.svc.cluster.local/knativetutorial/default" \
-X POST \
-H "Ce-Id: 1234" \
-H "Ce-Specversion: 1.0" \
-H "Ce-Type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration" \
-H "Ce-Source: curl" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"user" : {"email" : "mike.strong@email.com", "firstName" : "mike", "lastName" : ""}}'This will send a request to the broker using HTTP binary binding for cloud events. The cloud events information
are given http headers prefixed with ce-.
Since user’s last name is not set the workflow will reject processing due to invalid data
The already registered path
Already registered path consists of steps that will lead to fast finish without user registration.
Try it
Follow steps in the Details section to see the already registered path in action.
| Login to a curler pod that enables an easy access to the broker to send requests as it might not be exposed to external traffic (e.g. ingress). If your Knative broker is exposed to external traffic you can skip the curler step. |
Issue following curl command from the pod running within cluster so the broker url will be properly resolved. Main rule here is that there should be already user with same first and last name registered. For example that the happy path has been executed.
curl -v "http://broker-ingress.knative-eventing.svc.cluster.local/knativetutorial/default" \
-X POST \
-H "Ce-Id: 1234" \
-H "Ce-Specversion: 1.0" \
-H "Ce-Type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration" \
-H "Ce-Source: curl" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"user" : {"email" : "mike.strong@email.com", "firstName" : "mike", "lastName" : "strong"}}'This will send a request to the broker using HTTP binary binding for cloud events. The cloud events information
are given http headers prefixed with ce-.
Since user was already registered processing is stopped