Persistence
Automatiko by default runs without any persistent storage so it can be used without additional components. Though in many cases workflow instances are long lived and thus require storage to persist its state.
Automatiko comes with several options to chose from
-
File system based storage
-
Database based storage
-
Amazon DynamoDB based storage
-
Apache Cassandra based storage
-
MongoDB based storage
| More is on their way and as soon as they will be implemented they will be listed here. |
File system based storage
The most basic but quite powerful storage option is based on file system. This means each workflow instance will be stored in dedicated file in configured directory.
In addition to file itself, Automatiko will store some metadata that allows to more efficiently look up instances without loading it completely.
Depending on file system capabilities these metadata will be stored as
-
extended file attributes if file system supports it
-
dot filenext to the actual file as a fallback option when file system does not support extended attributes
Configuration
To use file system based perssitence your service must have following dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>io.automatiko.addons</groupId>
<artifactId>automatiko-filesystem-persistence-addon</artifactId>
</dependency>| Note that each persistence addon comes with job service implementation as well to provide persistence of timers defined in workflows |
Additional configuration should be placed in application.properties
| Property name | Environment variable | Description | Required | Default value | BuildTime only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.type |
Specify what persistence should be used |
No |
Yes |
||
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.filesystem.path |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_PERSISTENCE_FILESYSTEM_PATH |
Location on file system that will be used to store persistent state |
Yes |
No |
|
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.type |
Specifies type of jobs implementation to be used |
No |
Yes |
||
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.filesystem.path |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_FILESYSTEM_PATH |
Location on file system where jobs persistent state will be stored |
Yes |
No |
|
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.filesystem.threads |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_FILESYSTEM_THREADS |
Specifies how many threads should be used for jobs execution |
No |
1 |
No |
| This storage option can be used for pretty much any use case but it has certain drawbacks depending on the file system being used. It might not be the best option when horizontal scalability is important. |
Database based storage
Database based storage is mainly dedicated to cover Database record processing
as it requires workflow data objects to be
-
simple types
-
entities
-
collection of entities
Its main applicability is to store workflow state next to the data it is processing.
| Data model of the workflow becomes an entity as well, which on database level will be represented as table. |
Every workflow definition will be stored in dedicated table that is constructed based on workflow identifier and version. The table will also have all simple type data objects in the same table and reference any entity data objects.
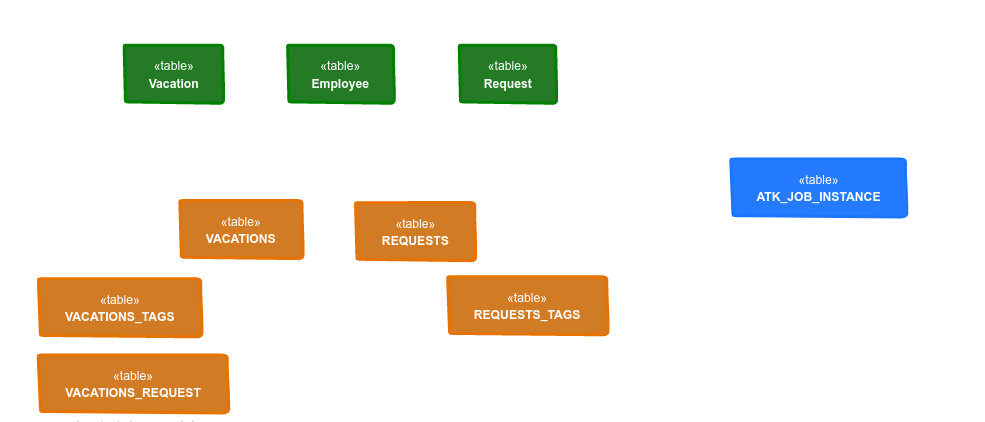
Green tables are those defined as data objects and annotated as entities. Orange tables are generated based on workflow definitions
-
vacations is the top level (public) process for handling vacation requests
-
requests is the sub workflow (private) that handles individual request
Blue table is used by jobs service that stores its data in db as well to support persistent timers defined in the workflow.
Data management
Since workflows operate on database records (entities defined as data objects) it has an option to manage these records. One of the important aspects is what should happen to the data after workflow instance completes?
There are two options provided by Automatiko
-
keep the data as they are at workflow instance completion
-
remove data that the workflow instance has worked with
| By default data is not removed at the completion of workflow instance |
Configuration
To use database based persistence your service must have following dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>io.automatiko.addons</groupId>
<artifactId>automatiko-db-persistence-addon</artifactId>
</dependency>| Note that each persistence addon comes with job service implementation as well to provide persistence of timers defined in workflows |
Additional configuration should be placed in application.properties
| Property name | Environment variable | Description | Required | Default value | BuildTime only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.type |
Specify what persistence should be used |
No |
Yes |
||
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.db.remove-at-completion |
Specifies if entities created during instance execution should be removed when instance completes |
No |
false |
Yes |
|
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.db.interval |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_DB_INTERVAL |
Specifies interval (in minutes) how often look for another chunk of jobs to execute |
No |
60 |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.db.threads |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_DB_THREADS |
Specifies how many threads should be used for job execution |
No |
1 |
No |
| Property name | Environment variable | Description | Required | Default value | BuildTime only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quarkus.datasource.db-kind |
Specify what kind of data base should be used |
Yes |
Yes |
||
quarkus.datasource.username |
QUARKUS_DATASOURCE_USERNAME |
Specify user name to be used to connect to data base |
Yes |
No |
|
quarkus.datasource.password |
QUARKUS_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD |
Specify password to be used to connect to data base |
Yes |
No |
|
quarkus.datasource.jdbc.url |
QUARKUS_DATASOURCE_JDBC_URL |
Specify url to be used to connect to data base |
Yes |
No |
Full configuration reference for data source can be found here
DynamoDB based storage
DynamoDB based storage allows to rely on Amazon managed DynamoDB. It allows to offload most of the storage heavy lifting (such as replication, scalability etc) to managed persistence service.
Automatiko takes advantages of highly scalable nature of DynamoDB that nicely fits into workflow data model - being key value based.
Every workflow definition will be stored in dedicated table that is constructed based on workflow identifier and version. That will result in each workflow definition to have dedicated storage location. Automatiko by default creates all required tables so there is no need to dive into the details but if such need arise automatic table creation can be disabled.
The table structure will have following attributes
-
InstanceId - (of type string) this is the unique id of each workflow instance
-
Content - (of type binary) this is the actual workflow instance serialized
-
Tags - (of type list) this is the workflow instance tags - it also includes
instance idandbusiness key -
PIStatus - current status of the workflow instance
-
VersionTrack - current version of the workflow instance (increment with each change)
| In addition when table is created it assigns default values for read and write capacity set to 10, it can be changed via configuration properties |
Configuration
To use DynamoDB based persistence your service must have following dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>io.automatiko.addons</groupId>
<artifactId>automatiko-dynamodb-persistence-addon</artifactId>
</dependency>| Note that each persistence addon comes with job service implementation as well to provide persistence of timers defined in workflows |
Additional configuration should be placed in application.properties
| Property name | Environment variable | Description | Required | Default value | BuildTime only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.type |
Specify what persistence should be used |
No |
Yes |
||
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.dynamodb.create-tables |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_PERSISTENCE_DYNAMODB_CREATE_TABLES |
Specifies if tables should be automatically created |
No |
true |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.dynamodb.read-capacity |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_PERSISTENCE_DYNAMODB_READ_CAPACITY |
Specifies read capacity to be applied to created DynamoDB tables |
No |
10 |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.dynamodb.write-capacity |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_PERSISTENCE_DYNAMODB_WRITE_CAPACITY |
Specifies write capacity to be applied to created DynamoDB tables |
No |
10 |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.dynamodb.create-tables |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_DYNAMODB_CREATE_TABLES |
Specifies if tables should be automatically created |
No |
true |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.dynamodb.read-capacity |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_DYNAMODB_READ_CAPACITY |
Specifies read capacity to be applied to created DynamoDB tables |
No |
10 |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.dynamodb.write-capacity |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_DYNAMODB_WRITE_CAPACITY |
Specifies write capacity to be applied to created DynamoDB tables |
No |
10 |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.dynamodb.interval |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_DYNAMODB_INTERVAL |
Specifies interval (in minutes) how often look for another chunk of jobs to execute |
No |
60 |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.dynamodb.threads |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_DYNAMODB_THREADS |
Specifies how many threads should be used for job execution |
No |
1 |
No |
| Property name | Environment variable | Description | Required | Default value | BuildTime only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quarkus.dynamodb.endpoint-override |
QUARKUS_DYNAMODB_ENDPOINT_OVERRIDE |
The endpoint URI with which the SDK should communicate |
Yes |
No |
|
quarkus.dynamodb.aws.region |
QUARKUS_DYNAMODB_AWS_REGION |
An Amazon Web Services region that hosts the given service |
Yes |
No |
|
quarkus.dynamodb.aws.credentials.type |
QUARKUS_DYNAMODB_AWS_CREDENTIALS_TYPE |
Configure the credentials provider that should be used to authenticate with AWS |
Yes |
No |
Full configuration reference for dynamodb can be found here
Apache Cassandra based storage
Apache Casandra based storage allows to rely on advanced distributed data store for highly available use cases. It enables use of multiple data centers to replicate workflow instance data securely to make it available in all available locations.
Every workflow definition will be stored in dedicated table that is constructed based on workflow identifier and version. That will result in each workflow definition to have dedicated storage location. Automatiko by default creates all required tables so there is no need to dive into the details but if such need arise automatic table creation can be disabled.
The table structure will have following attributes
-
InstanceId - (of type text) this is the unique id of each workflow instance
-
Content - (of type blob) this is the actual workflow instance serialized
-
Tags - (of type set) this is the workflow instance tags - it also includes
instance idandbusiness key -
PIStatus - current status of the workflow instance
-
VersionTrack - current version of the workflow instance (increment with each change)
In addition to tables, Automatiko will create key space as well with configured name. If name is not given then it
defaults to automatiko.
Automatic keyspace creation is most basic setup as it uses simple replication strategy with replication
factor set to 1. For more advanced (production like) use cases key space should be created manually and its name
should be given via configuration.
|
Next to tables, each workflow definition will get an index to be able to query more efficiently.
Configuration
To use Apache Cassandra based persistence your service must have following dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>io.automatiko.addons</groupId>
<artifactId>automatiko-cassandra-persistence-addon</artifactId>
</dependency>| Note that each persistence addon comes with job service implementation as well to provide persistence of timers defined in workflows |
Additional configuration should be placed in application.properties
| Property name | Environment variable | Description | Required | Default value | BuildTime only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.type |
Specify what persistence should be used |
No |
Yes |
||
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.cassandra.create-keyspace |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_PERSISTENCE_CASSANDRA_CREATE_KEYSPACE |
Specifies if keyspace should be automatically created |
No |
true |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.cassandra.create-tables |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_PERSISTENCE_CASSANDRA_CREATE_TABLES |
Specifies if tables should be automatically created |
No |
true |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.cassandra.keyspace |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_PERSISTENCE_CASSANDRA_KEYSPACE |
Specifies key space name to be used for tables |
No |
10 |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.cassandra.create-keyspace |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_CASSANDRA_CREATE_KEYSPACE |
Specifies if keyspace should be automatically created |
No |
true |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.cassandra.create-tables |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_CASSANDRA_CREATE_TABLES |
Specifies if tables should be automatically created |
No |
true |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.cassandra.keyspace |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_CASSANDRA_KEYSPACE |
Specifies key space name to be used for tables |
No |
10 |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.cassandra.interval |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_CASSANDRA_INTERVAL |
Specifies interval (in minutes) how often look for another chunk of jobs to execute |
No |
60 |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.cassandra.threads |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_CASSANDRA_THREADS |
Specifies how many threads should be used for job execution |
No |
1 |
No |
| Property name | Environment variable | Description | Required | Default value | BuildTime only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quarkus.cassandra.contact-points |
QUARKUS_CASSANDRA_CONTACT_POINTS |
Specify url to the cassandra data base |
Yes |
No |
|
quarkus.cassandra.local-datacenter |
QUARKUS_CASSANDRA_LOCAL_DATACENTER |
Specify data senter to be used on cassandra |
Yes |
No |
Full configuration reference for Apache Cassandra can be found here
MongoDB based storage
Document databases are very popular and makes a good fit in cloud environments. MongoDB based persistence addon allows to keep workflow information as a document. Most important part is that data objects of the workflow instance is stored as nested document and by that can be used as target of queries.
Every workflow definition will be stored in dedicated table that is constructed based on workflow identifier and version. That will result in each workflow definition to have dedicated storage location. Automatiko by default creates all required collections and default indexes so there is no need to dive into the details but if such need arise collections can be created up front.
The table structure will have following attributes
-
instanceId - (of type text) this is the unique id of each workflow instance
-
content - (of type binary) this is the actual workflow instance serialized
-
tags - (of type set) this is the workflow instance tags - it also includes
instance idandbusiness key -
piStatus - current status of the workflow instance
-
versionTrack - current version of the workflow instance (increment with each change)
-
variables - a nested document that represents all variables
Configuration
To use MongoDB based persistence your service must have following dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>io.automatiko.addons</groupId>
<artifactId>automatiko-mongodb-persistence-addon</artifactId>
</dependency>| Note that each persistence addon comes with job service implementation as well to provide persistence of timers defined in workflows |
Additional configuration should be placed in application.properties
| Property name | Environment variable | Description | Required | Default value | BuildTime only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.type |
Specify what persistence should be used |
No |
Yes |
||
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.mongodb.database |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_PERSISTENCE_MONGODB_DATABASE |
Name of the database where collections for workflows will be created |
Yes |
automatiko |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.type |
Specifies type of jobs implementation to be used |
No |
Yes |
||
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.mongodb.database |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_MONGODB_DATABASE |
Name of the database where collection for jobs (atk_jobs) will be created |
Yes |
automatiko |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.mongodb.interval |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_MONGODB_INTERVAL |
Specifies interval (in minutes) how often look for another chunk of jobs to execute |
No |
60 |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.jobs.mongodb.threads |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_JOBS_MONGODB_THREADS |
Specifies how many threads should be used for job execution |
No |
1 |
No |
| Property name | Environment variable | Description | Required | Default value | BuildTime only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quarkus.mongodb.hosts |
QUARKUS_MONGODB_HOSTS |
Configures the MongoDB server addressed (one if single mode). The addresses are passed as host:port. |
Yes |
No |
Full configuration reference for mongodb can be found here
Transaction log
| Use of transaction log comes with performance penalty as it records to disk each activity |
When using persistence, regardless what is the actual data store (file system, Cassandra, DynamoDB, MongoDB etc) there is always a risk that the service might crash while performing operations and before the result of the operation is written to data store.
At the same time, service can be one of the mission critical services that cannot effort to loose the work that was in flight. To allow to have more fault tolerance support to avoid lost work a transaction log can be enabled in the service to record individual steps and in case of a crash perform automatic recovery on next start of the service.
Transaction log records every activity of the workflow that is being executed and stores it in transaction log store. In case of a crash of the system, next start will look up into transaction log store to find in flight transactions. Every in flight transaction found will be automatically recovered from the last activity recorded meaning it won’t re-execute already performed activities and resume from last one directly. No need to have administrators to do any action to make this happen.
Worth noting is that recovery is done as part of the startup process which blocks and prevents from complete startup until recovery is completed. This is done on purpose to ensure no requests get in the way during recovery. This is important from health check probes point of view especially readiness check as it might lead to service being killed by orchestrator (e.g. Kubernetes) during recovery. Recovery is usually very fast but if there are many instances to be recovered or the actions recovery starts from is blocking for long time it might affect overall startup time.
| Configure readiness check accordingly to avoid intermittent pod evictions during long recovery. |
Configuration
Transaction log is disabled by default and must be explicitly enabled. Once enabled it must provide a folder location where transaction logs will be written. This folder must be a persistent folder that will survive service crashes.
| Property name | Environment variable | Description | Required | Default value | BuildTime only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.transaction-log.enabled |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_PERSISTENCE_TRANSACTION_LOG_ENABLED |
Enables transaction log for workflows to always record activities that are performed to automatically recover after crash |
No |
false |
No |
quarkus.automatiko.persistence.transaction-log.folder |
QUARKUS_AUTOMATIKO_PERSISTENCE_TRANSACTION_LOG_FOLDER |
Location on file system that will be used to store transaction log entries |
Yes (if transaction log is enabled) |
No |
Transaction log store
Transaction log records every activity execution and places that into transaction log store. Currently there is only one transaction log store based on file system that records individual instances grouped by transaction id. It is not the most efficient storage option but already provides significant value but with more performance overhead.
Transaction log store can be provided by application developers by implementing
io.automatiko.engine.api.uow.TransactionLogStore interface. In addition there are plans to also implement other
store implementation out of the box.