Workflow as a Function Flow (WaaFF)
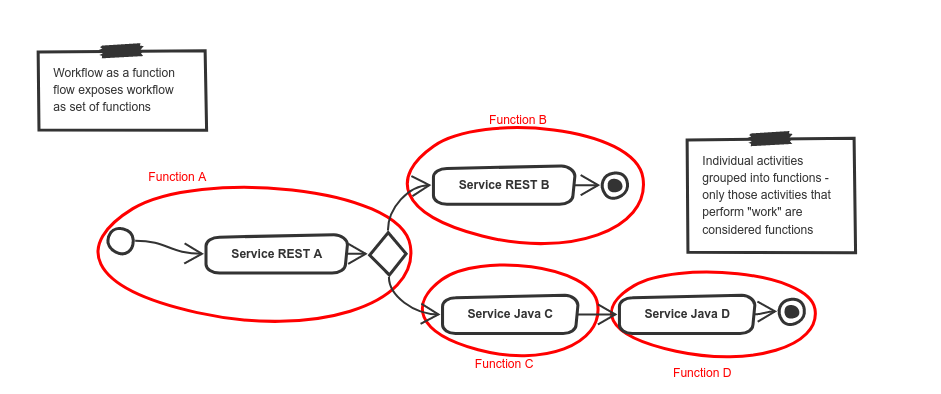
Workflow as Function Flow is a more advanced extension to Workflow as a Function which breaks the workflow into many different functions.
A function, in workflow terms, is a single executing activity. This single
activity can be grouped with other activities that do not actually perform work but
can be one of the following:
-
start or end of the workflow
-
control logic (gateways)
-
pass-through activities
In the diagram above again we see the same workflow example as used in the WaaS and WaaF scenarios. This time however we can break it up into multiple functions:
-
function
Adefines the start of the workflow instance function and it consists of three activities (start,service A, and the`gateway`) -
function
Bdefines the second function and it consists of two activities, namelyService REST Bandend. It is invoked when a decision was made to invoke "Service REST B". -
function
Cdefines the third function which is invoked when a decision is made to invokeService Java Cand. It consists only a single activity (Service Java C) -
function
Dis the last function that is invoked directly afterFunction Cand consists of two activities (Service Java Dandend)
All functions (except "Function A" which defines the workflow start) are invoked automatically based on the execution context. This means that a function, during its execution, can identify the next function(s) to be invoked. This decision is influenced by both the workflow definition as well as workflow data.
Workflow as a function flow always exchanges data as events in CloudEvent format.
It target deployment environment is Knative Eventing in order to take advantage of
its routing capabilities for events.
Workflow as a function flow allows to use special custom attributes on workflow definition and activities.
| Name | Description | Type | Default if not set |
|---|---|---|---|
functionType |
Provides a custom function type that will be used instead of generated value |
String |
Function type will be generated based on package name of the workflow, workflow id and activity name
e.g. |
functionFlowContinue |
Instructs the execution to not produce new function for a node that has this parameter |
Boolean |
false |
functionFilter |
Additional filter attributes to be used to match on cloud event attributes (mainly used by Google Cloud Run environment) |
String |
Using functionType custom attribute users can have full control on how the generated function will be identified.
Functions are identified by Cloud Event type attribute and this attribute is also used as part of Knative trigger
filter definition.
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: userregistration
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: user-registrationSending events to other services and functions
Workflow as a Function Flow exchanges events to invoke activities of the workflow. Though there might be a need to push events to other services and functions that are not belonging to the workflow. For that purpose using intermediate or end message throw events should be used.
Using message events to send events to other services/functions allows us to have control over what data are
being sent. That is based on data mapping on the message event. The mapped data object will be put into the
Cloud Event data attribute as JSON.
functionType custom attribute can be used to gain control over the type attribute of the sent event. If not set
then the value of the type attribute will be generated based on
-
package name
-
workflow id
-
message name
It’s recommended to always use functionType custom attributes for message events
|
Receiving events from other services and functions
Similar to the use case to send events to other services/functions (that are not part of the workflow),
intermediate catch message events should be used. It allows to define the message and it’s data type
that will be used to convert Cloud Event’s data attribute of the incoming event to a data object that
will be used within workflow execution.
An important aspect is how to find the right workflow instance that the event should target? To address this there are two ways
-
explicitly provide id of the workflow instance as part of the
subjectattribute of the cloud event -
configure correlation on the message defined inside the workflow definition
| Using correlation might result in triggering 0 or more workflow instances that the correlation matches. |
Another worth knowing fact is how workflow as a function flow informs about the workflow instance that
sends the events. That is done via source attribute of the cloud event and is in following format
`
type attribute of function being executed / workflow instance id
`
And example of this would like like this io.automatiko.examples.userRegistration/24b1e99b-f917-4c5f-af02-6d81da06719b
With this whoever consumes the event can easily extract the identifier of the workflow instance and use it
as subject attribute to reply to the same instance.
Get started
To get started with Workflow as a Function Flow users can take advantage of ready to use maven archetype to generate the project structure
-
automatiko-function-flow-archetypee - Tailored project type for function flow use case backed by Knative
Here is a ready to use command to generate project based on automatiko-function-flow-archetype
mvn archetype:generate \
-DarchetypeGroupId=io.automatiko.archetypes \
-DarchetypeArtifactId=automatiko-function-flow-archetype \
-DarchetypeVersion=LATEST \
-DgroupId=com.acme.workflows \
-DartifactId=workfow-functionConfigure project
Once the project is bootstrapped, it needs to be configured according to the needs. There are two places where configuration is done
-
pom.xml- definition of the dependencies and Automatiko addons to be used -
application.properties- all configuration parameters are defined there (found insrc/main/resourcesdirectory)
A complete configuration of Automatiko specific configuration parameters can be found here, Quarkus specific configuration parameters can be found here.
Examples
Following is a list of examples that can be tried out to see Workflow as a Function Flow in action
| Name | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
user registration |
BPMN based workflow for user registration that uses Swagger PetStore as user repository. Ready to be deployed to any Knative (both service and eventing) environment |
|
user registration |
Serverless workflow based workflow for user registration that uses Swagger PetStore as user repository. Ready to be deployed to any Knative (both service and eventing) environment |
|
user registration |
BPMN based workflow for user registration that uses Swagger PetStore as user repository. Ready to be deployed to Google Cloud Run environment |